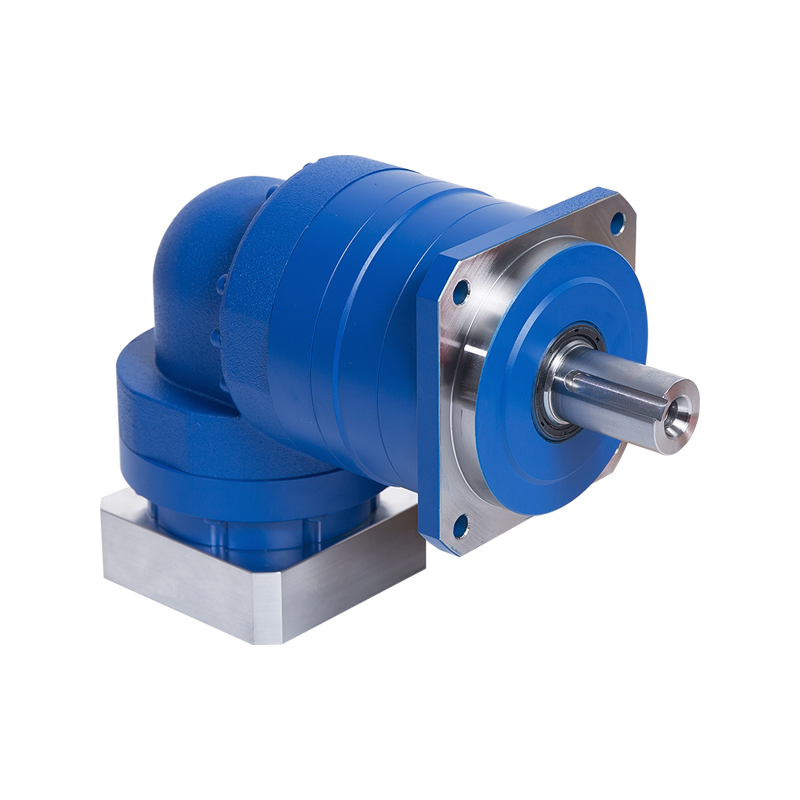
Servo Motor MKT Precision Planetary Reducer
Cat:MK series planetary reducer
Meet the needs of customers with high precision requirements for semiconductor devices, automation equipment, machine tools, etc.Applicable to: Door d...
See DetailsWhen selecting a planetary gear reducer for a specific application, several key factors should be considered:
Torque Requirements:
Maximum Torque: Ensure the reducer can handle the maximum torque your application will generate.
Continuous vs. Peak Torque: Consider both continuous and peak torque requirements, as the reducer must withstand peak loads without damage.
Gear Ratio:
Desired Gear Ratio: Determine the required gear ratio to achieve the desired output speed and torque. Planetary gear reducers offer a wide range of gear ratios, which can affect performance and efficiency.
Speed:
Input and Output Speeds: Match the input and output speeds with your application’s requirements. Ensure the reducer can operate efficiently at these speeds.
Efficiency:
Power Losses: Consider the efficiency of the gear reducer, as higher efficiency reduces power losses and improves overall performance.
Size and Weight:
Space Constraints: Evaluate the physical size and weight of the reducer to ensure it fits within the space constraints of your application.
Load Capacity: Make sure the size and weight do not compromise the load capacity of the gear reducer.
Durability and Reliability:
Material and Construction: Check the materials and construction quality to ensure long-term durability and reliability under your operating conditions.
Environmental Conditions: Consider factors such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to contaminants, and select a reducer that can withstand these conditions.
Backlash:
Accuracy Requirements: If precise positioning is required, choose a reducer with minimal backlash. High precision applications demand reducers with low backlash.
Lubrication and Maintenance:
Lubrication Type: Understand the lubrication requirements and maintenance schedules. Choose a reducer with lubrication needs that fit your maintenance capabilities.
Service Life: Evaluate the expected service life and maintenance requirements to ensure they align with your application’s needs.
Load Characteristics:
Type of Load: Consider the nature of the load (e.g., constant, variable, shock loads) and select a reducer that can handle these conditions effectively.
Cost and Budget:
Cost vs. Performance: Balance cost with performance requirements. Sometimes a higher upfront cost may result in lower overall operational costs due to better efficiency and durability.
Mounting and Integration:
Compatibility: Ensure the reducer’s mounting options and shaft configurations are compatible with your application’s design and integration requirements.
Noise and Vibration:
Operating Environment: If noise and vibration are concerns, select a gear reducer designed to minimize these issues.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can select a planetary gear reducer that meets your application’s specific requirements and ensures optimal performance and reliability.